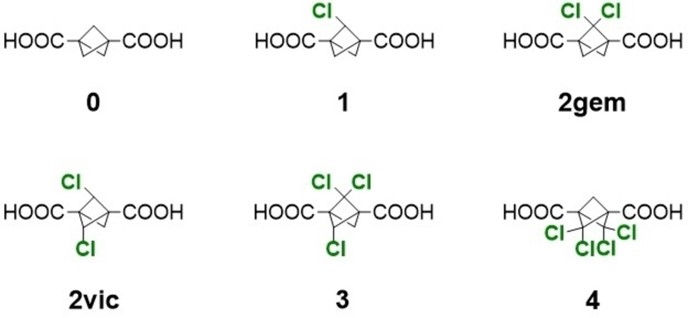
The scientific team from IOCB Prague and J. Heyrovský Institute investigated the electrochemical reduction of five derivatives of bicyclo[1.1.1]pentane-1,3-dicarboxylic acid containing one to four chlorine substituents on methylene bridges by cyclic voltammetry and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy.
The electrochemical removal of the chlorine atoms from the studied derivatives brings alternative possibilities for the synthesis of new chlorinated cages. Besides that, a distinct difference in reaction mechanism was found once the two carboxylic groups attached to the cages were substituted with corresponding methyl esters.
The results of the studies accompanied by DFT calculations have been published in ChemElectroChem with Jiří Kaleta as the first author and led to the invitation for the month's cover picture.

The original paper
- Kaleta, J.; Hromadová, M.; Pospíšil, L. Electrochemical Cleavage of Carbon-Chlorine Bonds in Multiply Bridge-Chlorinated Bicyclo[1.1.1]pentane-1,3-dicarboxylic Acids. ChemElectroChem 2021, 8, 1-8. https://doi.org/10.1002/celc.202100372