Termites are among the most abundant terrestrial animals and their success is undoubtedly due to their ability to feed on dead trees. However, the cellulose diet is deficient in many vital components including linoleic acid, which is an essential nutrient for most animals. Researchers from Robert Hanus and Iva Pichová Groups from IOCB Prague wanted to understand how did it happen that termites became independent of the dietary supply of this polyunsaturated fatty acid.
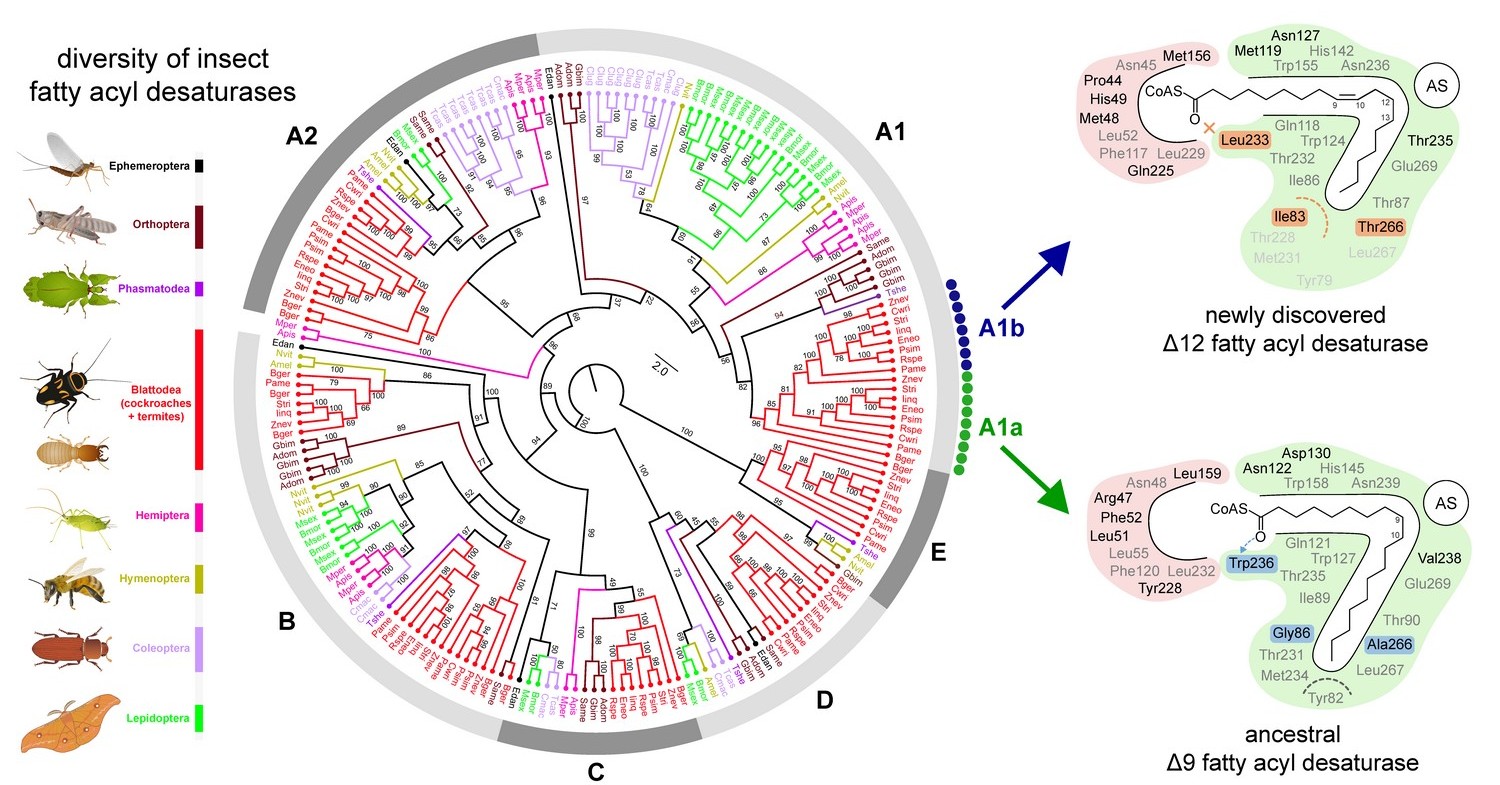
They discovered that termites possess a Δ12 fatty acyl desaturase, which effectively converts the ubiquitous oleic acid into linoleic acid. This enzyme evolved via ancient duplication of a gene coding for Δ9 fatty acyl desaturase and gained a novel function. This event took place in termite ancestors roughly 160 million years ago and represents a crucial preadaptation that paved the way for the current ecological dominance of termites.
Read the paper: Macháček, S., Tupec, M., Horáček, N., Halmová, M., Roy, A., Machara, A., Kyjaková, P., Lukšan, O., Pichová, I., Hanus, R. (2023). Evolution of Linoleic Acid Biosynthesis Paved the Way for Ecological Success of Termites. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2023, 40, msad087. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msad087