The role of α-synuclein interactions with lipid membrane in Parkinson’s disease
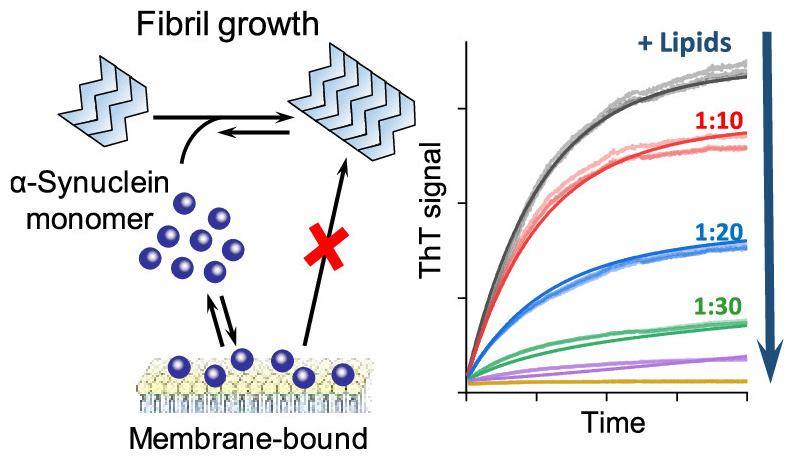
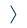
Parkinson’s disease is a progressive disorder of the central nervous system affecting movements. α-Synuclein is a neuronal protein consisting of 140 amino acids, which is closely connected with Parkinson’s disease. During Parkinson’s disease, α-synuclein aggregates, forming amyloid fibrils that accumulate in the midbrain. The interactions of α-synuclein with lipid membranes regulate the fibrillization process.
A team of scientists led by Volodymyr Shvadchak from IOCB Prague applied the environment-sensitive fluorescent dyes to study the influence of model lipid membranes on the kinetics of α-synuclein fibrils formation. The analysis showed that the formation of fibrils from α-synuclein monomers is strongly delayed by small amounts of lipids. Besides, the α-synuclein monomers bound to the membrane are not involved in the fibrils elongation process. The study was published in ACS Chemical Neuroscience.
Read the paper:
- Kurochka, A. S.; Yushchenko, D. A.; Bouř, P.; Shvadchak, V. V. Influence of Lipid Membranes on α-Synuclein Aggregation. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2021, 12, 825-830. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschemneuro.0c00819