Inhibition of the protein-protein interaction in influenza polymerase PA-PB1 subunit interface
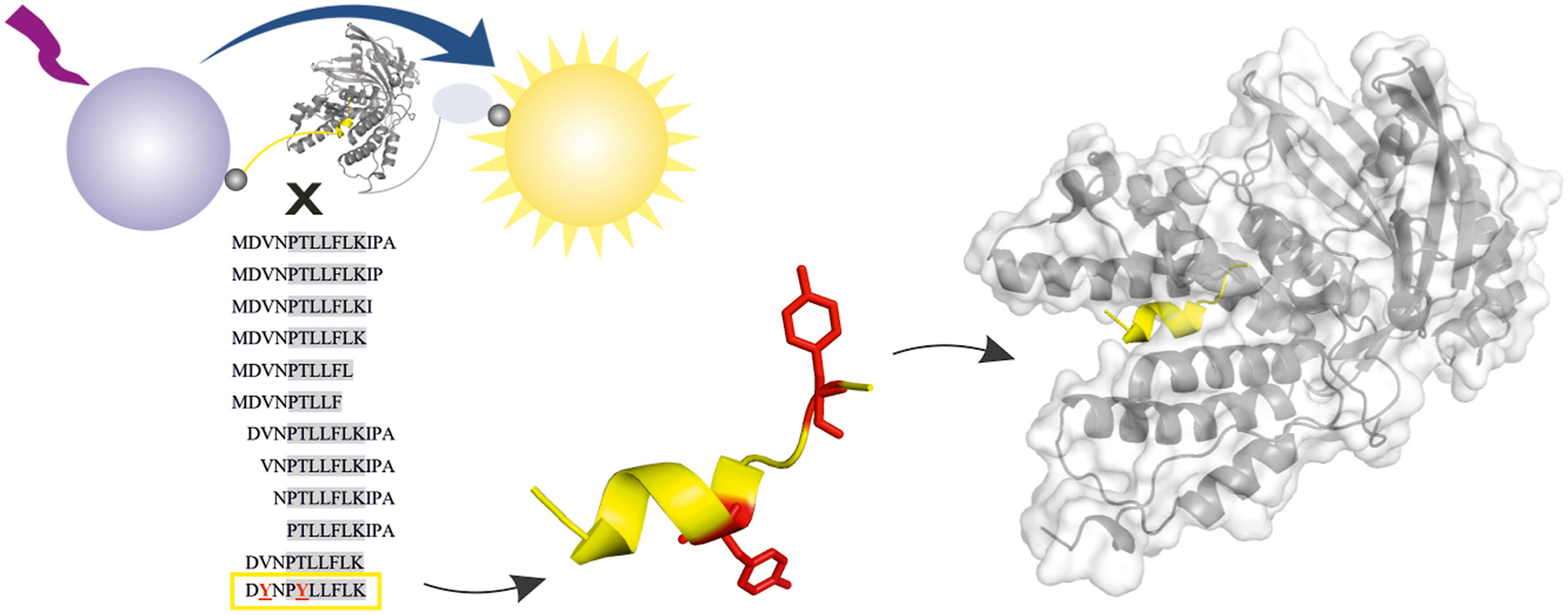
The influenza virus remains life-threatening, causing hundreds of thousands of deaths each year. The virus uses an RNA-dependent-RNA polymerase to replicate within a host organism. The active influenza polymerase is composed of three subunits (PA, PB1, and PB2) whose assembly is inter-dependent and has to be precisely coordinated to the minutest detail. Consequently, the inhibition of protein-protein interaction between PA and PB1 represents a new target for drug development.
The multidisciplinary team led by Milan Kožíšek and Jan Konvalinka from IOCB Prague in collaboration with scientists from the Institute of Molecular Genetics of the CAS developed a new AlphaScreen assay to find short peptides acting as nanomolar inhibitors of polymerase PA-PB1 subunit interface. Importantly, this area is conserved within a broad range of the influenza A strains. The results published in Antiviral Research provide also X-ray structural information useful for novel structure-assisted drug design.
The results published in Antiviral Research provide also X-ray structural information useful for novel structure-assisted drug design.
X-ray structure of the influenza polymerase PA C-terminal domain and an optimized PB1-like inhibitor
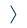
The video captures X-ray structures of the PA C-terminal domain in a complex with an optimized PB1-like inhibitor (decapeptide). In contrast to regular PPIs, the present PA-PB1 subunit interface interaction involves only a dozen of amino acid residues of the PB1 peptide that are embedded in a deep hydrophobic pocket of the PA domain. This unique feature gives us the chance to mimic PB-1 in the interface with drugs and thus efficiently stop the assembly of the influenza RNA-polymerase.
Read the paper:
- Hejdánek, J.; Radilová, K.; Pachl, P.; Hodek, J.; Machara, A.; Weber, J.; Řezáčová, P.; Konvalinka, J.; Kožíšek, M., structural characterization of the interaction between the C-terminal domain of the influenza polymerase PA subunit and an optimized small peptide inhibitor. Antiviral Research 2021, 185, 104971. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104971