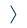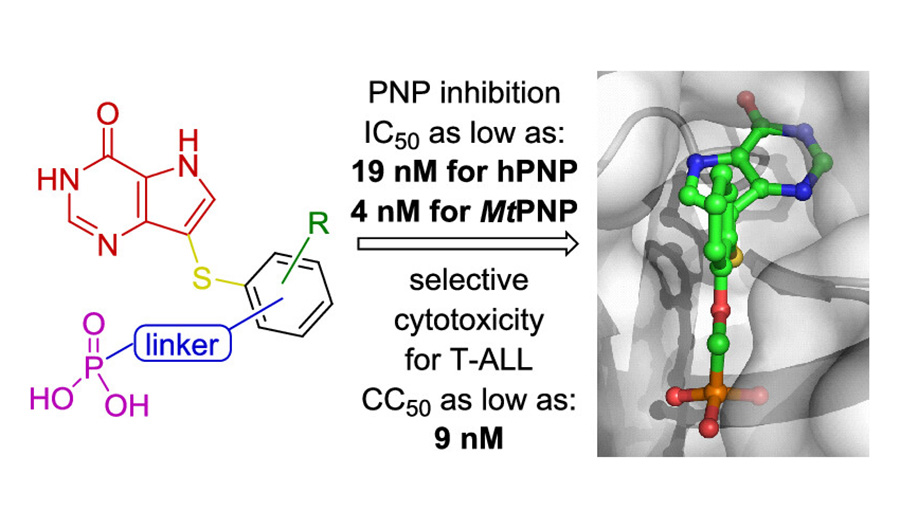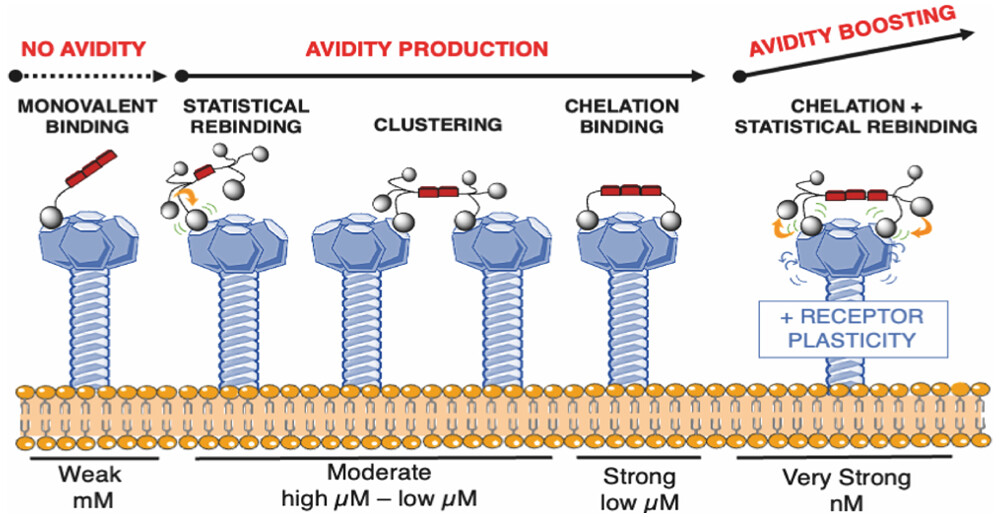
The cGAS-STING pathway recognizes cytoplasmic DNA that can be a sign of viral infection or cellular damage. The activation of the pathway triggers immune mechanisms which fight the viruses and also have anticancer potential. Therefore, small molecules targeting the immune cGAS-STING pathway are explored in antiviral and antitumor therapy.
The HBV Cure Group at IOCB Prague previously prepared a series of synthetic cyclic dinucleotides (CDNs), the agonists of STING protein, that activated the cGAS-STING pathway at lower doses than natural CDN. However, these CDNs are charged and require a transporter to enter the cell. The researchers have now prepared a series of lipophilic prodrugs of candidate CDNs that diffuse freely through the cell membrane. The prodrug moiety is subsequently cleaved, releasing the active CDNs into the cytoplasm. The prodrug also lowers the dose required for the cGAS-STING pathway activation up to 1000x compared to the parent CDNs, thus improving its therapeutic potential.
The researchers led by Gabriel Birkuš, with Markéta Pimková Polidarová and Petra Břehová as the first authors, published their results in the Journal of Medicinal Chemistry.
Read the paper:
- Pimková Polidarová, M.; Břehová, P.; Kaiser, M. M.; Smola, M.; Dračínský, M.; Smith, J.; Marek, A.; Dejmek, M.; Šála, M.; Gutten, O.; Rulíšek, L.; Novotná, B.; Brázdová, A.; Janeba, Z.; Nencka, R.; Boura, E.; Páv, O.; Birkuš, G. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Phosphoester and Phosphorothioate Prodrugs of STING Agonist 3′,3′-c-Di(2′F,2′dAMP). Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2021, 64, 7596-7616. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c00301